# Matrix (m rows * n cols)
- 2차원 배열: matrix[m][n]
- Space complixity = S(m,n) = m*n → 얼마만큼의 기억장소를 필요로하는지 나타내는 척도
* 배열이 int 형일 때, S(m,n) = m*n*4
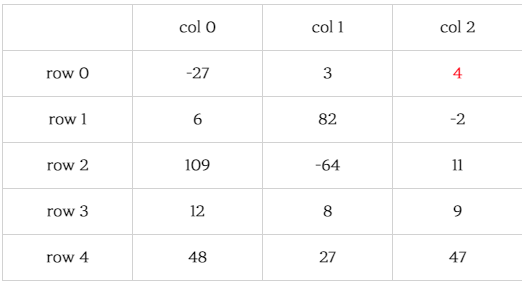
ex) 4 : 배열 안의 원소를 entry라고 하며 배열을 사용해 나타낼 때는 matrix[0][2]와 같이 나타냄
# Sparse Matrix
- 희소 행렬: 행렬의 값이 대부분 0인 행렬 → 저장 공간은 큰데 의미있는 값은 적음
- A[m,n]: 대부분의 값이 0이며 이 행렬을 효과적으로 저장하는 방법을 찾아야함 → 중요한 목표
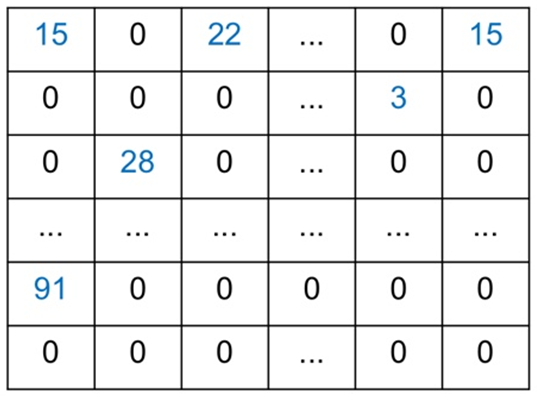
# Sparse Matrix solution
- 0이 아닌 element만 저장한다
- 3튜플을 가지는 배열을 활용한다 (row,col,value) → 구조체 배열 사용
- 구조체 배열 0번째 인덱스에는 행,열의 개수와 0이 아닌 값(유의미한 수)의 전체 개수를 저장함
ex) a를 3튜플을 가지는 배열이라고 할 때,
> a[0].row: 행의 갯수를 저장
> a[0].col: 열의 갯수를 저장
> a[0].value: 0이 아닌 유의미한 값의 개수를 저장
> a[1]: 0이 아닌 element들이 저장되며 왼쪽에서 오른쪽, 위에서 아래 순서대로 저장해 나감

# 3 - tuple struct
# define MAX_TERMS 1001
struct term {
int row;
int col;
int value;
};
struct term a[MAX_TERMS];
# Sparse Matrix 구현
[코드]
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAX_TERMS 101 /* maximum number of terms + 1 */
typedef struct {
int col;
int row;
int value;
} term;
term a[MAX_TERMS];
int main()
{
// sparse matrix of class 5x6 with 6 non-zero values
int sparseMatrix[6][6] =
{
{ 15 , 0 , 0 , 22 , 0, 15 },
{ 0 , 11 , 3 , 0 , 0, 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , -6 , 0, 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0, 0 },
{ 91 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0, 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 28 , 0 , 0 , 0 }
};
term *tuple;
// Finding total non-zero values in the sparse matrix
int size = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < 6; row++)
for (int column = 0; column < 6; column++) {
if (sparseMatrix[row][column] != 0)
size++;
}
tuple = (term*)malloc(sizeof(term)*(size + 1));
// Generate Triple
tuple[0].row = 6;
tuple[0].col = 6;
tuple[0].value = size;
int i = 1;
for (int row = 0; row < 6; row++){
for (int column = 0; column < 6; column++) {
if (sparseMatrix[row][column] != 0) {
tuple[i].row = row;
tuple[i].col = column;
tuple[i].value = sparseMatrix[row][column];
i++;
}
}
}
// Triple Repesentation
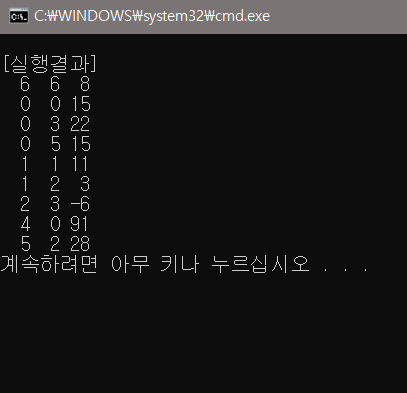
printf("\n[실행결과]\n%3d%3d%3d\n", tuple[0].row, tuple[0].col, tuple[0].value);
for (int i = 1; i < size + 1; i++) {
printf("%3d%3d%3d\n", tuple[i].row, tuple[i].col, tuple[i].value);
}
return 0;
}
[실행결과]
# Space complexity for a normal matrix (m*n)
- S(m, n) = 3(t+1) < m*n
* 이때 t는 유의미한 값(0이 아닌 값)의 개수이다
'Study > Data Structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [DS] Queue(큐) & Circular Queue(순환 큐) (0) | 2021.08.31 |
|---|---|
| [DS] Stack (스택) (0) | 2021.08.31 |
| [DS] 자료구조 개념 및 구현 Chapter 4 연습문제 (0) | 2021.08.26 |
| [DS] 알고리즘 분석 (0) | 2021.08.26 |
| [DS] 자료구조 개념 및 구현 Chapter 3 연습문제 (0) | 2021.08.26 |
